Connection to Azure MSSQL
If you do not have the MSSQL Server NATIVE SRV, MSSQL Server NATIVE SRV PDO and MSSQL Server ODBC drivers enabled, check below our documentation on how to enable both in Scriptcase for connection.
- To enable the PDO DBLIB: Click here
ATTENTION: If you do not have an Azure MSSQL Server base created, check how to create it by clicking here.
Creating a connection to Scriptcase
See below how to create a connection in your Scriptcase project, using the Enabled Driver (MSSQL Server NATIVE SRV or MSSQL Server NATIVE SRV PDO) and the Azure MSSQL Server database.
1 - Access a project from your Scriptcase.
2 - Click the New Connection icon to create a connection
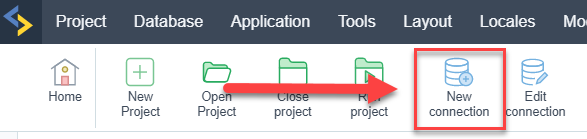
or access the Database > New connection menu.
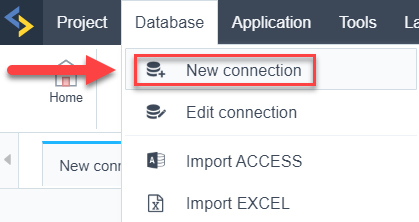
After that, a screen will appear with all database connections.
3 - Select the Microsoft Azure connection.

4 - And choose the Azure SQL database.

Connection
Enter the parameters for connecting to your Azure MSSQL Server database as follows:
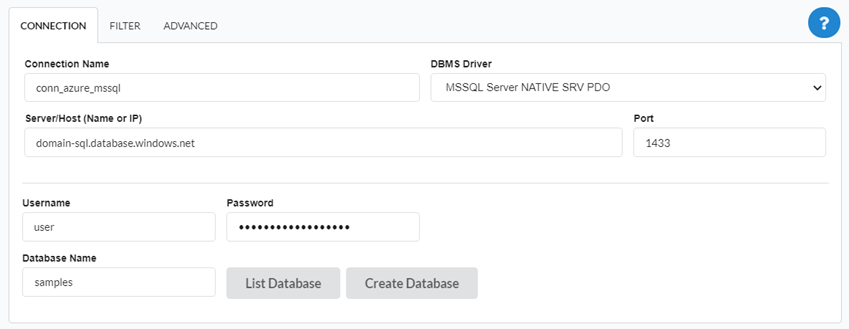
-
Connection name: Define the name of your new connection. By default, Scriptcase adds the prefix conn along with the database name.
-
DBMS Driver: Select the MSSQL Server Driver to connect. In this example, we use the PDO DBLIB Driver.
- Server/Host (Name or IP): Enter the domain of the Azure server where the database is installed.
-
EX:
domain-sql.database.windows.net -
Port: Enter the port to connect to the MSSQL Server. By default, the port defined is 1433.
- Database Name: List and select the database you will connect to.
-
EX:
samples -
Username: Inform the user to authenticate the connection to your database.
-
Password: Enter the password to complete the authentication process.
- Test connection: Click this button to get a response to the Scriptcase request to find out if the parameters entered are correct.
Security
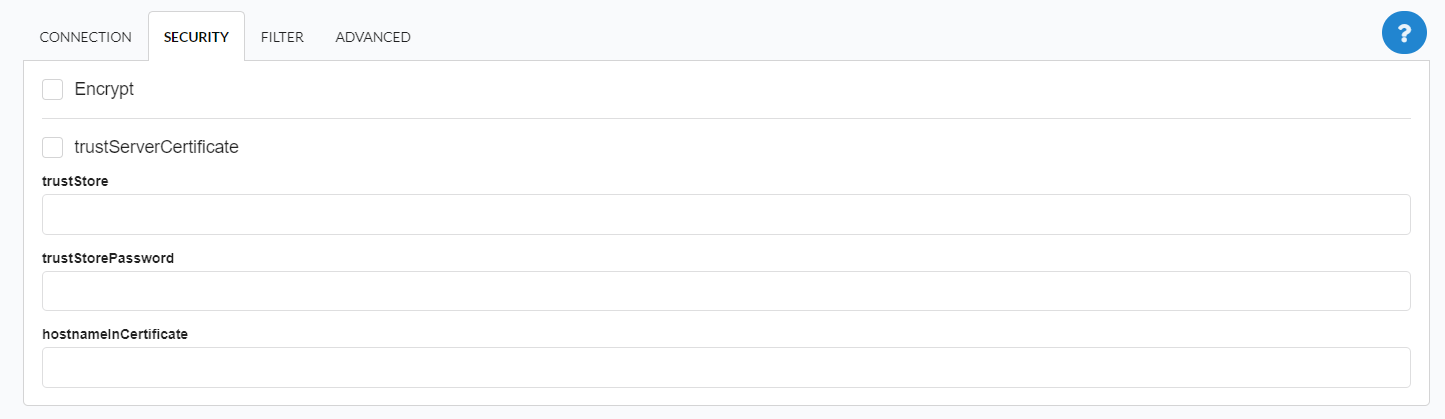
Security tab, where the connection encryption settings are defined.
-
Encrypt
This property specifies whether communication with the SQL server should be encrypted. To enable encryption, you must set this property to “true”. This ensures that data sent between the client and server is protected by encryption.
-
trustservercertificate
Set to “true” to specify that the driver does not validate the server’s TLS/SSL certificate.
If “true”, the server’s TLS/SSL certificate is automatically trusted when the communication layer is encrypted using TLS.
-
trustStore
The path (including the file name) to the certificate’s trustStore file. The trustStore file contains the list of certificates that the client trusts.
When this property is not specified or is set to null, the driver relies on the trust manager factory query rules to determine which certificate store to use.
-
trustStorePassword
The password used to verify the integrity of trustStore data.
If the trustStore property is set but the trustStorePassword property is not set, the integrity of the trustStore is not checked.
-
hostnameInCertificate
The hostname to use to validate the SQL Server TLS/SSL certificate.
This property allows you to specify the expected hostname in the SQL server certificate. This is useful to ensure that the connection is only made to the correct server and not to a malicious server that may be using an invalid certificate.
Note: This property is used in combination with the encrypt/authentication properties and the trustServerCertificate property. This property affects certificate validation if the connection uses TLS encryption and trustServerCertificate is set to “false”. Ensure that the value passed to hostNameInCertificate matches the Common Name (CN) or DNS name in the Subject Alternative Name (SAN) in the server certificate for a TLS connection to be successful. For more information about encryption support, see Understanding encryption support.
Filter
Accessing this tab, you can configure which Database items will be displayed on the connection, depending on the owner or not.
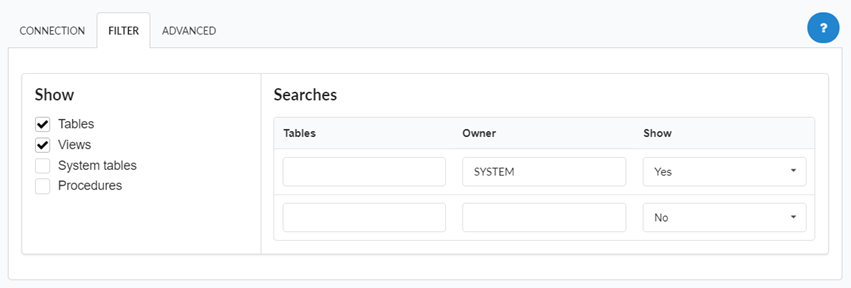
Show
It allows the connection to see tables, views, system tables and procedures depending on the items selected by the user. By default, the items Tables and Views are already selected by Scriptcase.
- Tables: Selecting this option, the tables in your database will be displayed.
- By default, Scriptcase enables this option .
- By default, Scriptcase enables this option .
- Views: By selecting this option, the views of your database will be displayed.
- By default, Scriptcase enables this option .
- By default, Scriptcase enables this option .
-
System Tables: Selecting this option, the system tables of your database will be displayed.
- Procedures: By selecting this option, the procedures of your database will be displayed.
Searches
Allows you to define which tables and owners are displayed.
- Tables: You can define in this option which tables will be displayed. The configuration can contain a
PREFIX%%or name of the tables to display.- By default, Scriptcase leaves this option empty .
- EX:
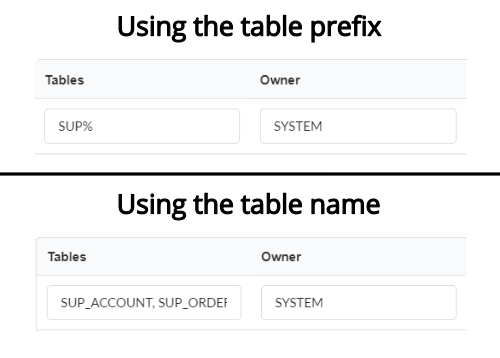
- Owner: Inform the user who sees the tables informed for display.
- User must be capitalized as in the example above .
- User must be capitalized as in the example above .
- View: Choose whether to display the tables for the informed owner.
NOTE: By using table filtering, you eliminate unnecessary tables for your project and improves the performance of your database connection.
Advanced
In this tab, you have access to specific settings for the connection. The settings made in this session impact the data display and application performance.
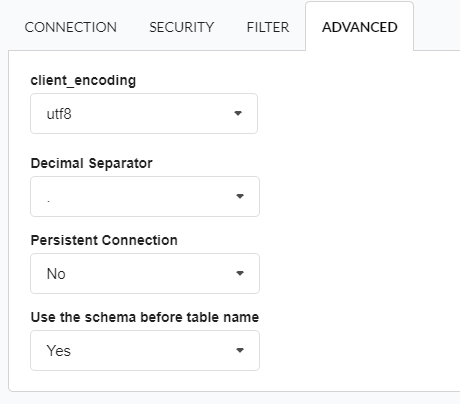
- client_encoding: Select the encoding used in your database. In the example above, we use the client_encoding utf8.
- The utf8 charset is set by default.
- The utf8 charset is set by default.
- Decimal Separator: Select the type of separator for decimal records, between comma and period.
- By default, the
.dot is selected as a separator .
- By default, the
- Persistent Connection: Define whether connections will be terminated after the execution of your scripts in Scriptcase applications.
- By default, Scriptcase disables this option .
- By default, Scriptcase disables this option .
- Use the schema before the table name: Define whether the database schema will be displayed before the table names.
- By default, Scriptcase enables this option.
